
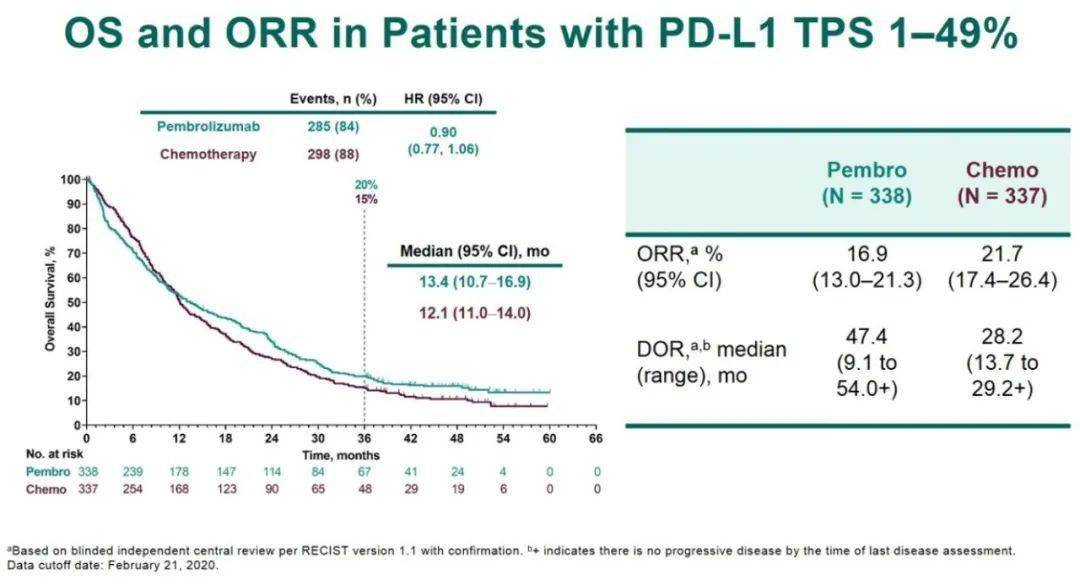
12.1 months), although the study was not powered for superiority or non-inferiority for the TPS 1–49% subset. An exploratory analysis showed that the overall survival in the TPS 1–49% group treated with pembrolizumab appears similar but not superior to chemotherapy (13.4 vs.
However, the results for Keynote 42 should be viewed with caution for tumors with TPS 1–49% as the superiority of pembrolizumab compared to chemotherapy for all patients with PD-L1 TPS ≥1% was likely driven by the subset of patients with PD-L1 TPS ≥50%. Keynote 42 also confirms the results of Keynote 24 with superior efficacy and less toxicity for pembrolizumab compared to chemotherapy for NSCLC with TPS ≥50%.
Keynote 042 trial#
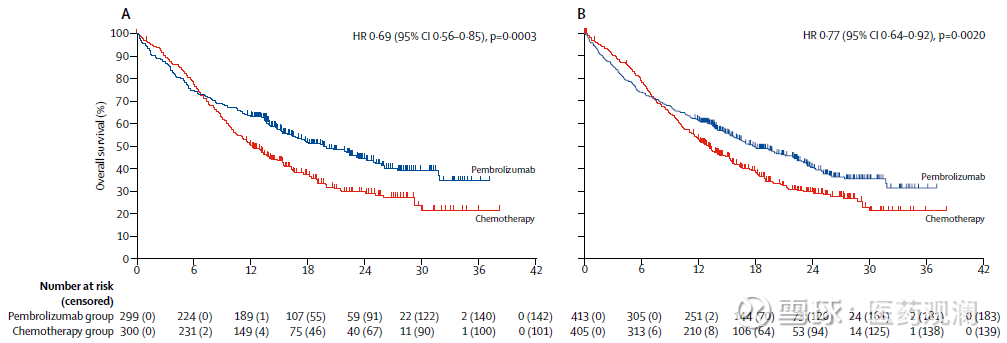
Keynote 42 is a pivotal phase III trial that established pembrolizumab monotherapy as a front-line therapeutic option for any non-small cell lung cancer with a TPS PDL-1 score ≥1%. The toxicity profile was significantly better with pembrolizumab compared to chemotherapy, with grade 3 or higher adverse events occurring in 18% vs. Only 20% of patients in the chemotherapy arm received immune checkpoint blockade at time of progression while many patients receiving initial pembrolizumab therapy would have access to second-line chemotherapy. Importantly, the trial did not allow cross over to pembrolizumab as part of the protocol. The median overall survival among patients who received pembrolizumab monotherapy for tumors with TPS ≥50%, ≥20% and ≥1% was 20, 17.7 and 16.7 months with hazard ratios of 0.69, 0.77 and 0.81 respectively compared to chemotherapy.
In the primary outcome, the trial showed superiority of single agent pembrolizumab over chemotherapy across all PD-L1 positive TPS subgroups. This was an open label, randomized international trial in 32 countries involving 1,274 patients. platinum doublet chemotherapy in patients with previously untreated metastatic or locally advanced squamous or non-squamous NSCLC and a PD-L1 TPS of ≥1% ( 4). report the second interim analysis of Keynote 42 which evaluated the use of pembrolizumab monotherapy vs. However, questions remain regarding the benefit of immune checkpoint blockade in comparison to chemotherapy for patients whose tumors have a low or intermediate PD-L1 TPS (1–49%). In the frontline treatment setting, Keynote 24 showed the superiority of pembrolizumab over chemotherapy in a highly selected group of patients with a PD-L1 TPS score greater than or equal to 50% ( 3). However, only a portion of patients will receive benefit from ICB and the PD-L1 tumor proportion score (TPS) has emerged as a biomarker that predicts clinical benefit ( 2).
Immune therapy with PD-L1 checkpoint blockade (ICB) has changed the landscape of treatment for NSCLC ( 1). Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): a randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Ran Mo (Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Nanjing, China).Ĭomment on: Mok TSK, Wu YL, Kudaba I, et al. Email: and Peer Review: This article is commissioned and reviewed by the Section Editor Dr. Duke University Medical Center, 25178 Morris Bldg, 20 Medicine Circle, Box 3198, Durham, NC 27710, USA.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
